Gist – India’s National Blockchain Framework (NBF) is a government-led digital infrastructure designed to build trust and transparency in governance. Launched in 2024, its core platform, the Vishvasya Blockchain Stack, enables secure, tamper-proof record-keeping across multiple sectors.
The NBF is already transforming services by verifying over 34 crore documents, securing medicine supply chains, and modernizing judiciary and property systems. This initiative aims to reduce fraud, streamline bureaucracy, and position India as a global leader in using blockchain for efficient and accountable public service.
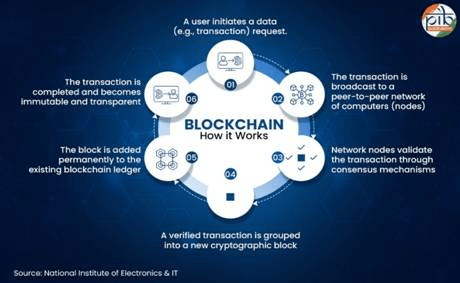
Imagine a digital ledger, not held by one single authority like a bank or a government office, but copied and distributed across a secure network of computers. Every transaction, every record added to this ledger is encrypted, time-stamped, and linked to the one before it. To change a single entry, you wouldn’t just have to break into one computer; you’d have to alter it on every single computer in the network simultaneously, which is practically impossible. This is the core idea behind blockchain—a technology that creates verifiable trust without the need for a middleman.
For a country like India, with a vast population and complex governance systems, this technology is a game-changer. It addresses critical challenges like document fraud, bureaucratic delays, and a lack of transparency. Recognizing this potential, the Government of India has developed the National Blockchain Framework (NBF), a unified, indigenous platform to transform public service delivery.
What is Blockchain in Simple Terms?
At its heart, a blockchain is a shared, unchangeable digital ledger. Think of it as a communal notebook that everyone in a trusted group has a copy of. When a new transaction occurs (e.g., “A issues a certificate to B”), it is written as a new line in everyone’s notebook. This line is locked cryptographically and linked to the previous line. If someone tries to fraudulently change a line in their own copy, it won’t match the thousands of other copies, and the change will be rejected by the network.
Key Characteristics:
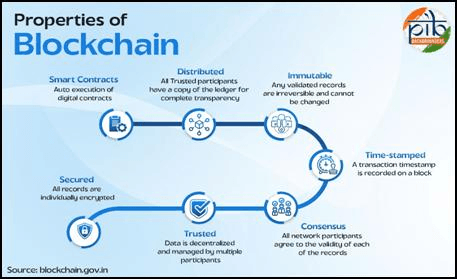
- Transparency: Authorized participants can view the transactions.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be altered or deleted.
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the entire ledger.
- Security: The distributed and encrypted nature makes it highly secure.
The NBF primarily uses a Private/Permissioned Blockchain, meaning it’s not open to the public. Only verified and authorized government entities and stakeholders can participate, ensuring data confidentiality and control while building trust among them.
The Pillars of the National Blockchain Framework (NBF)
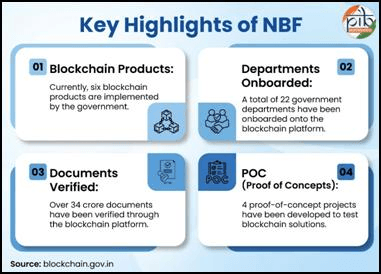
Launched in September 2024 with a budget of ₹64.76 crore, the NBF is not a single product but an entire ecosystem designed to foster blockchain adoption. Its core components are:
1. The Engine: Vishvasya Blockchain Stack
This is the indigenous technological backbone of the NBF. “Vishvasya” implies trust, which is exactly what it aims to provide. Its features include:
- Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS): Government departments don’t need to build their own complex blockchain infrastructure from scratch. They can simply “rent” this ready-made, secure platform to deploy their applications, much like how we use cloud services today.
- Distributed Infrastructure: The stack is deployed across National Informatics Centre (NIC) data centres in Bhubaneswar, Pune, and Hyderabad. This makes the network resilient—if one centre has an issue, the others keep the system running.
- Open APIs: These are standard connectors that allow the blockchain to seamlessly integrate with existing e-governance systems, making adoption smooth and efficient.
2. The Sandbox: NBFLite
Innovation needs a safe space to experiment. NBFLite is a sandbox version of the full blockchain stack designed for startups, students, and academia. It allows them to learn, prototype, and test blockchain applications without the cost or risk of using the live national framework. It comes with pre-built templates for common use cases like supply chain and digital certificates.
3. The Authenticator: Praamaanik
In a world flooded with mobile apps, how can you be sure an app is genuine and not a scam designed to steal your data? Praamaanik is a blockchain-based solution that verifies the authenticity of mobile applications. By scanning an app, users can match its details against the official, tamper-proof records on the blockchain, ensuring it is legitimate.
4. The Gateway: National Blockchain Portal
This is the central online hub for all information on India’s blockchain strategy. It outlines the government’s vision, supports standardization, and fosters cross-sector adoption of the technology.
Blockchain in Action: Real-World Applications Transforming India
The true test of the NBF is its practical application. Several “chains” are already live, demonstrating tangible benefits:
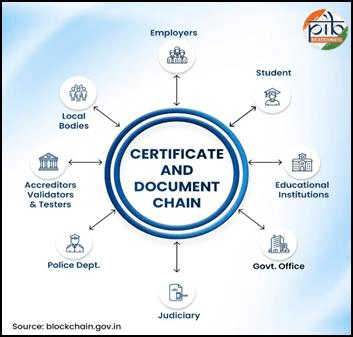
- Certificates & Document Chain: Fighting Fraud
- Problem: Fake degree certificates, caste certificates, and income documents.
- Blockchain Solution: Documents issued by authorities (like the Central Board of Secondary Education for academic certificates) are stored on the blockchain. Employers or universities can instantly verify their authenticity with a digital check. As of October 2025, over 34 crore documents have been securely verified this way.
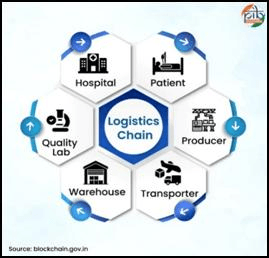
- Logistics Chain: Securing Supply Chains
- Problem: Counterfeit goods, especially in critical areas like medicines.
- Blockchain Solution: The movement of goods is recorded at every step. A key example is Karnataka’s ‘Aushada’ system for drug supply. A patient can scan a medicine and trace its entire journey from the manufacturer to the hospital, including quality checks, ensuring it is not spurious.
- Judiciary & ICJS Chain: Modernizing Justice
- Problem: Delays in serving court notices, summons, and managing case records.
- Blockchain Solution: Judicial documents are stored immutably, allowing for secure electronic delivery and reducing manual delays. The Inter-operable Criminal Justice System (ICJS) integrates records across police, courts, and prisons, creating a unified, tamper-proof digital ecosystem.
- Property Chain: Bringing Clarity to Land Records
- Problem: Land disputes, opaque ownership history, and fraudulent transactions.
- Blockchain Solution: Every property transaction is permanently recorded. A prospective buyer can see the entire history of ownership and transactions, reducing litigation and bringing much-needed transparency to one of India’s most complex sectors.
Building a Blockchain-Ready India: Strategy and Skilling
The government’s approach is holistic, focusing not just on technology but also on regulation and human capital.
- Strategic Roadmap: MeitY has a clear National Strategy on Blockchain, setting both short and long-term goals for integration across sectors.
- Centre of Excellence (CoE): The NIC’s CoE provides government departments with consultancy, training, and support to develop and test their blockchain ideas before full-scale rollout.
- Regulatory Adoption: Key bodies are already integrating blockchain:
- TRAI uses it to combat spam calls and SMS, allowing end-to-end tracking of commercial messages.
- RBI is piloting the Digital Rupee (e₹), a central bank digital currency using blockchain for instant, transparent payments.
- NSDL uses it for monitoring corporate debentures, enhancing investor confidence with a tamper-proof audit trail.
- Capacity Building: To create a skilled workforce, the government has launched programs like:
- Skill Development for Officials: Training over 21,000 government officials in blockchain.
- PG Diploma in FinTech & Blockchain: A comprehensive course for professionals.
- BLEND & FutureSkills Prime: Online courses for students and professionals to build proficiency.
The Road Ahead
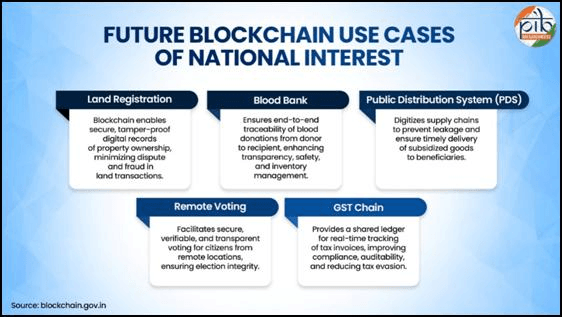
The future is promising, with several new use cases being explored through Proof of Concepts (POCs). These include:
- Land Records: For creating indisputable ownership histories.
- Blood Bank Management: For transparent tracking of donations from donor to recipient.
- GST Chain: For real-time, transparent monitoring of tax transactions.
- Public Distribution System (PDS): For securing the supply chain of essential commodities.
Conclusion
India’s National Blockchain Framework is a visionary step towards building a digital infrastructure rooted in trust, transparency, and efficiency. By providing a common platform, encouraging innovation, and building capacity, the framework is moving the nation beyond the hype to practical, governance-improving applications. In line with the vision of a Digital India and an Aatmanirbhar Bharat, this initiative positions India not just as a user, but as a potential global leader in leveraging blockchain technology for inclusive and transformative governance.
Visit: National Blockchain Framework
Read PIB – National Blockchain Framework – Strengthening Governance through Blockchain Technology
Visit https://inworldnews.com/ for more

