Introduction of Self Help Group – SHG
An Self Help Group – SHG is a small, voluntary association of 10-20 people from similar socio-economic backgrounds, who come together for a common purpose of saving, mutually agreeing to contribute to a common fund, and meeting their emergency needs through self-governance and mutual help.
Key Characteristics of an SHG under DAY-NRLM:
- Composition: Typically consists of 10-20 members, preferably all women from poor households.
- Voluntary: Formation is based on the principle of voluntary association.
- Homogeneity: Members are from similar social and economic backgrounds, fostering trust and solidarity.
- Self-Help and Mutual Aid: The core philosophy is to solve their common problems through collective action.
- Self-Governed: The group manages its own affairs, makes its own decisions, and is democratically run.
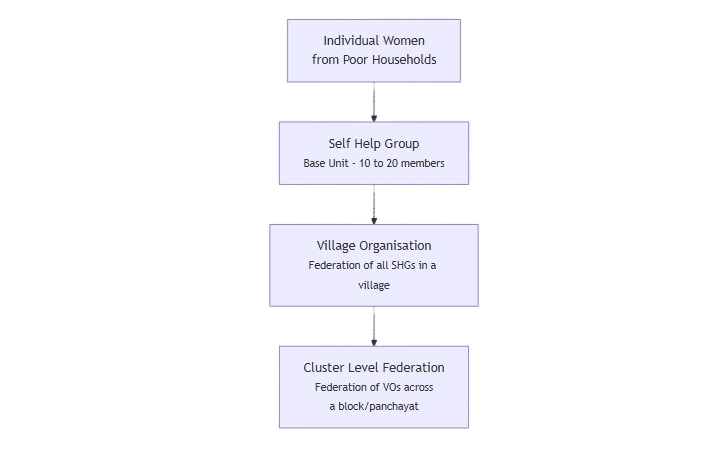
The Formation and Graduation Process (Institutional Architecture)
DAY-NRLM follows a structured, federated model to build strong institutions of the poor.
1. Self Help Group (SHG) – The Base
- Members save a small amount regularly (e.g., ₹10-₹50 per week).
- They use their pooled savings to give small, internal loans to members for immediate needs (health, consumption, small expenses) at a mutually decided interest rate.
- This builds financial discipline and a credit history.
2. Village Organisation (VO) – The First Level Federation
- Once there are enough SHGs in a village (typically 10-15 or more), they are federated into a Village Organisation (VO).
- The VO is a registered body that represents the collective voice of all SHGs in the village.
- It manages a common fund, provides support to SHGs, and interfaces with banks and government departments.
3. Cluster Level Federation (CLF) – The Higher Federation
- VOs from a cluster of villages (a block or a panchayat) come together to form a Cluster Level Federation (CLF).
- The CLF operates at a larger scale, managing larger funds, taking up bigger livelihood projects, and providing capacity-building support to VOs and SHGs.
This structure is visually represented below:
Key Functions and Activities of SHGs under DAY-NRLM
1. Financial Inclusion:
- Regular Savings: Inculcates the habit of thrift and capital accumulation.
- Internal Lending (Credit Corpus): Provides immediate, collateral-free loans for emergencies and small income-generation activities.
- Bank Linkage: A core strategy of DAY-NRLM is to link SHGs with formal banks (Bank Linkage Program). This allows SHGs to access larger loans (often at subsidized interest rates) after demonstrating creditworthiness through their internal lending.
2. Social Mobilization and Empowerment:
- Creates a platform for women to come together, discuss their problems, and find collective solutions.
- Builds confidence, leadership skills, and decision-making abilities among women who were previously confined to their homes.
- Addresses social issues like domestic violence, alcoholism, child marriage, and education of girls.
3. Livelihoods Enhancement:
- SHGs are used as a platform to promote both farm-based and non-farm-based livelihoods.
- Members can access loans for purchasing livestock, seeds, small equipment, or setting up micro-enterprises.
- DAY-NRLM provides skill development training (through its RoSCTL component – Recruitment of Skilled Community Cadres for Training and Livelihoods) to enhance employability.
4. Access to Entitlements and Schemes:
- SHGs and VOs act as a collective to demand and access their rights and government welfare schemes related to pensions, food security, housing, and employment (MGNREGA).
5. Community Resilience:
- The group provides a strong social safety net during crises like illness, death, or natural disasters.
Critical Support provided by DAY-NRLM to SHGs
DAY-NRLM does not just form groups and leave them. It provides intensive support through:
- Community Resource Persons (CRPs): Successful members from existing SHGs are trained to become CRPs. They act as mentors and facilitators for new SHGs, making the process more credible and sustainable.
- Revolving Fund (RF): After a minimum period of good performance, SHGs are eligible for a one-time Revolving Fund from the government to strengthen their capital base.
- Capital Subsidy (or Interest Subvention): To make loans cheaper, the government provides an interest subvention, effectively reducing the interest burden on SHGs for loans taken from banks.
- Capacity Building: Continuous training is provided on book-keeping, leadership, enterprise development, and social issues.
Impact of SHGs under DAY-NRLM
The model has been transformative in many parts of India, leading to:
- Enhanced Household Incomes: Through access to credit and livelihoods.
- Reduced Vulnerability: The savings and loan system acts as a buffer against shocks.
- Women’s Empowerment: Significant increase in women’s decision-making power within the household and in the community.
- Financial Literacy: Millions of rural women have become financially literate and capable of dealing with banks.
- Strengthened Grassroots Democracy: The federated structure creates a powerful, decentralized institution of the poor.
In summary, SHGs under DAY-NRLM are much more than just savings and credit groups. They are powerful instruments of social and economic change, empowering rural women to break the cycle of poverty and become agents of their own development.
For More Information Please Visit : NRLM.gov.in
Visit https://inworldnews.com/ for more

